Swift 2.0 —— 集合类型
0.Swift 语言提供 Arrays 、Sets 和 Dictionaries 三种基本的集合类型用来存储集合数据。数组(Arrays)是有序数据的集。集合(Sets)是无序无重复数据的集。字典(Dictionaries)是无序的键值对的集。
1.Swift 语言中的 Arrays、Sets 和 Dictionaries 中存储的数据值类型必须明确。这意味着我们不能把不正确的数据类型插入其中。
2.Swift 的 Arrays、Sets 和 Dictionaries 类型被实现为泛型集合。
3.如果创建一个 Arrays、Sets 或 Dictionaries 并且把它分配成一个变量,这个集合将会是可变的。这意味着我们可以在创建之后添加更多或移除已存在的数据项来改变这个集合的大小。如果我们把 Arrays、Sets 或 Dictionaries 分配成常量,那么它就是不可变的,它的大小不能被改变。
4.在我们不需要改变集合大小的时候创建不可变集合是很好的习惯。如此 Swift 编译器可以优化我们创建的集合。
5.写 Swift 数组应该遵循像 Array<Element> 这样的形式,其中 Element 是这个数组中唯一允许存在的数据类型。我们也可以使用像 [Element] 这样的简单语法。尽管两种形式在功能上是一样的,但是推荐较短的那种。
6.Swift 中的 Array 类型还提供一个可以创建特定大小并且所有数据都被默认的构造方法。我们可以把准备加入新数组的数据项数量(count)和适当类型的初始值(repeatedValue)传入数组构造函数:
|
|
7.我们可以使用加法操作符( + )来组合两种已存在的相同类型数组。新数组的数据类型会被从两个数组的数据类型中推断出来:
|
|
8.我们可以使用字面量来进行数组构造,这是一种用一个或者多个数值构造数组的简单方法。字面量是一系列由逗号分割并由方括号包含的数值:
|
|
9.可以使用数组的只读属性 count 来获取数组中的数据项数量:
|
|
10.使用布尔值属性 isEmpty 作为检查 count 属性的值是否为 0 的捷径:
|
|
11.也可以使用 append(_:) 方法在数组后面添加新的数据项:
|
|
除此之外,使用加法赋值运算符( += )也可以直接在数组后面添加一个或多个拥有相同类型的数据项:
|
|
12.可以用下标来获取或改变某个已有索引值对应的数据值
|
|
13.还可以利用下标来一次改变一系列数据值,即使新数据和原有数据的数量是不一样的。下面的例子把 "Chocolate Spread","Cheese" 和 "Butter" 替换为 "Bananas" 和 "Apples":
|
|
14.调用数组的 insert(_:atIndex:) 方法来在某个具体索引值之前添加数据项:
|
|
15.类似的我们可以使用 removeAtIndex(_:) 方法来移除数组中的某一项。这个方法把数组在特定索引值中存储的数据项移除并且返回这个被移除的数据项(我们不需要的时候就可以无视它):
|
|
16.如果我们只想把数组中的最后一项移除,可以使用 removeLast() 方法而不是removeAtIndex(_:) 方法来避免我们需要获取数组的 count属性。
|
|
17.我们可以使用 for-in 循环来遍历所有数组中的数据项
|
|
18.如果我们同时需要每个数据项的值和索引值,可以使用 enumerate() 方法来进行数组遍历。enumerate() 返回一个由每一个数据项索引值和数据值组成的元组。我们可以把这个元组分解成临时常量或者变量来进行遍历:
|
|
19.集合(Set)用来存储相同类型并且没有确定顺序的值。当集合元素顺序不重要时或者希望确保每个元素只出现一次时可以使用集合而不是数组。
20.一个类型为了存储在集合中,该类型必须是可哈希化的–也就是说,该类型必须提供一个方法来计算它的哈希值。一个哈希值是 Int 类型的,相等的对象哈希值必须相同,比如 a==b,因此必须 a.hashValue == b.hashValue。
Swift 的所有基本类型(比如 String,Int,Double 和 Bool)默认都是可哈希化的,可以作为集合的值的类型或者字典的键的类型。没有关联值的枚举成员值(在枚举有讲述)默认也是可哈希化的。
21.Swift 中的 Set类型被写为 Set<Element>,这里的 Element 表示 Set 中允许存储的类型,和数组不同的是,集合没有等价的简化形式。
|
|
22.你可以使用数组字面量来构造集合,并且可以使用简化形式写一个或者多个值作为集合元素。
|
|
23.一个 Set 类型不能从数组字面量中被单独推断出来,因此 Set 类型必须显式声明。然而,由于 Swift 的类型推断功能,如果你想使用一个数组字面量构造一个Set 并且该数组字面量中的所有元素类型相同,那么你无须写出 Set的具体类型。favoriteGenres 的构造形式可以采用简化的方式代替:
|
|
24.为了找出一个 Set 中元素的数量,可以使用其只读属性 count:
|
|
25.使用布尔属性 isEmpty 作为一个缩写形式去检查 count 属性是否为 0 :
|
|
25.你可以通过调用 Set 的 insert(_:) 方法来添加一个新元素:
|
|
26.你可以通过调用 Set 的 remove(_:) 方法去删除一个元素,如果该值是该 Set 的一个元素则删除该元素并且返回被删除的元素值,否则如果该 Set 不包含该值,则返回 nil。另外,Set 中的所有元素可以通过它的 removeAll() 方法删除。
|
|
27.使用 contains(_:) 方法去检查 Set 中是否包含一个特定的值:
|
|
28.你可以在一个 for-in 循环中遍历一个Set中的所有值。
|
|
29.Swift 的 Set 类型没有确定的顺序,为了按照特定顺序来遍历一个 Set 中的值可以使用 sort() 方法,它将根据提供的序列返回一个有序集合。
|
|
30.下面的插图描述了两个集合-a和b-以及通过阴影部分的区域显示集合各种操作的结果
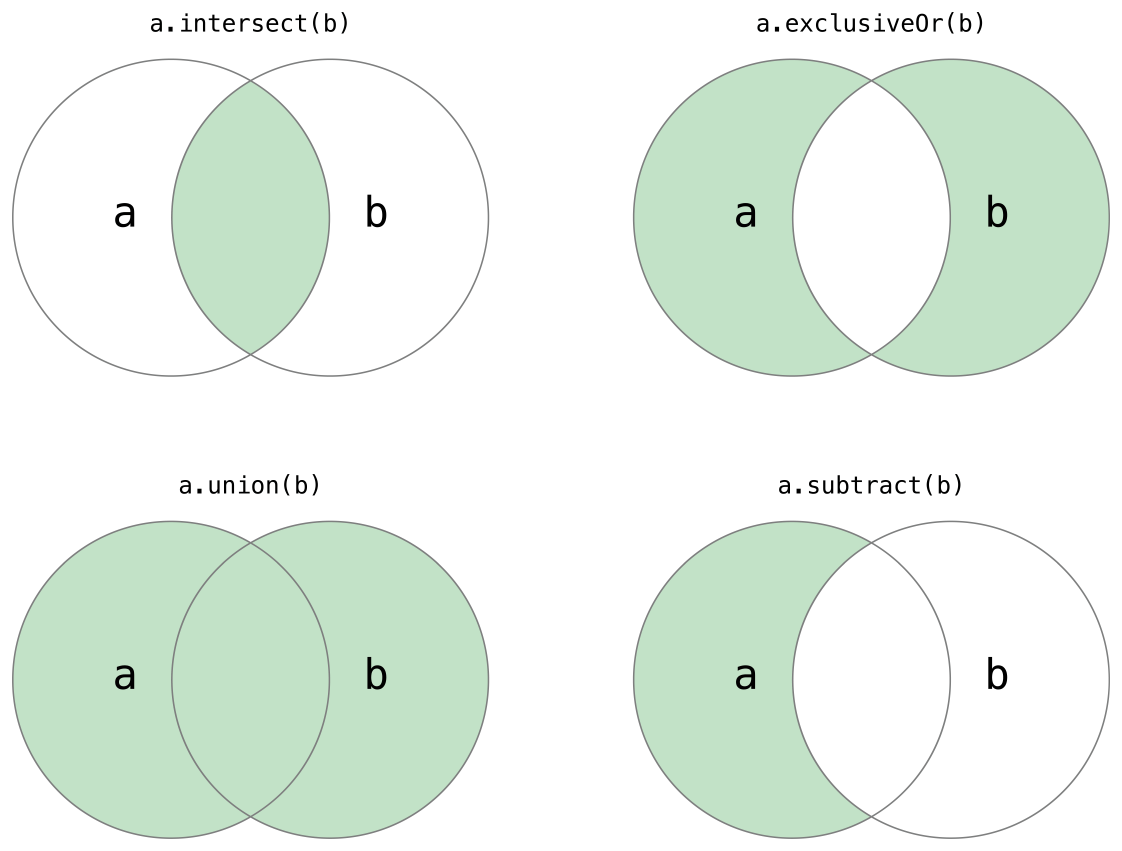
- 使用
intersect(_:)方法根据两个集合中都包含的值创建的一个新的集合。 - 使用
exclusiveOr(_:)方法根据在一个集合中但不在两个集合中的值创建一个新的集合。 - 使用
union(_:)方法根据两个集合的值创建一个新的集合。 - 使用
subtract(_:)方法根据不在该集合中的值创建一个新的集合。
|
|
31.下面的插图描述了三个集合- a,b 和 c,以及通过重叠区域表述集合间共享的元素。集合 a 是集合b的父集合,因为 a 包含了 b 中所有的元素,相反的,集合 b 是集合 a 的子集合,因为属于 b 的元素也被 a 包含。集合 b 和集合 c 彼此不关联,因为它们之间没有共同的元素。
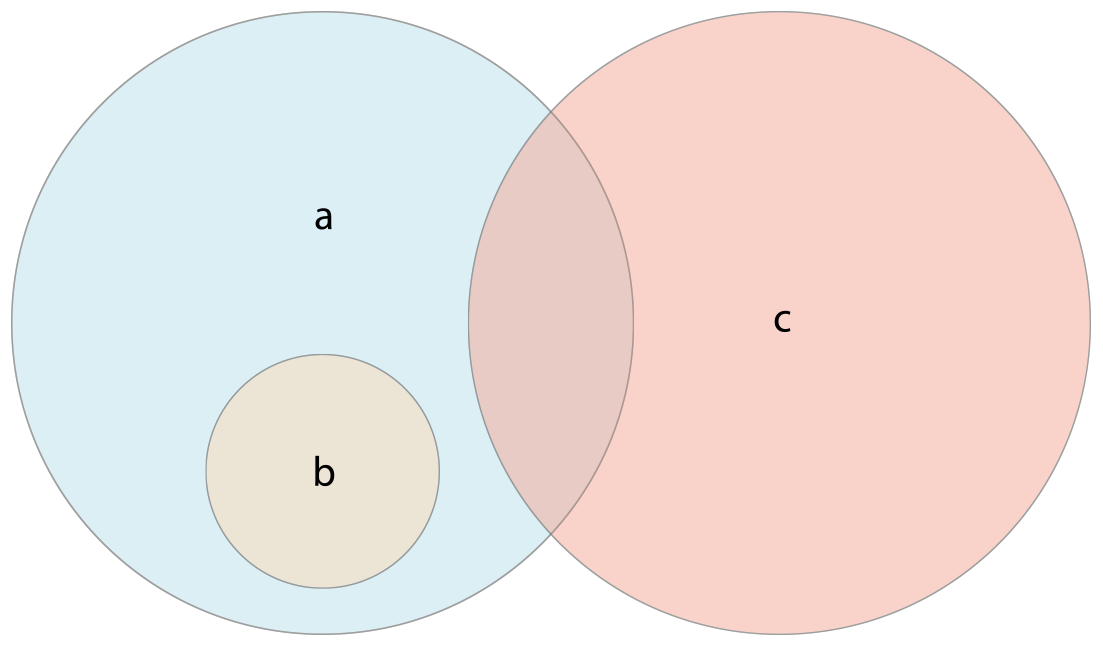
- 使用“是否相等”运算符(
==)来判断两个集合是否包含全部相同的值。 - 使用
isSubsetOf(_:)方法来判断一个集合中的值是否也被包含在另外一个集合中。 - 使用
isSupersetOf(_:)方法来判断一个集合中包含另一个集合中所有的值。 - 使用
isStrictSubsetOf(_:)或者isStrictSupersetOf(_:)方法来判断一个集合是否是另外一个集合的子集合或者父集合并且两个集合并不相等。 - 使用
isDisjointWith(_:)方法来判断两个集合是否不含有相同的值。
|
|
32.Swift 的字典使用 Dictionary<Key, Value> 定义,其中 Key 是字典中键的数据类型,Value 是字典中对应于这些键所存储值的数据类型。
33.一个字典的 Key 类型必须遵循 Hashable 协议,就像 Set 的值类型。
34.字面量形式声明
|
|
34.和数组一样,我们可以通过字典的只读属性 count来获取某个字典的数据项数量:
|
|
35.使用布尔属性 isEmpty 来快捷地检查字典的 count 属性是否等于 0 :
|
|
36.我们也可以在字典中使用下标语法来添加新的数据项。可以使用一个恰当类型的键作为下标索引,并且分配恰当类型的新值:
|
|
37.作为另一种下标方法,字典的 updateValue(_:forKey:) 方法可以设置或者更新特定键对应的值。就像上面所示的下标示例,updateValue(_:forKey:) 方法在这个键不存在对应值的时候会设置新值或者在存在时更新已存在的值。和上面的下标方法不同的,updateValue(_:forKey:) 这个方法返回更新值之前的原值,如果为新添加的则返回空。这样使得我们可以检查更新是否成功。
|
|
38.我们也可以使用下标语法来在字典中检索特定键对应的值。因为有可能请求的键没有对应的值存在,字典的下标访问会返回对应值的类型的可选值。如果这个字典包含请求键所对应的值,下标会返回一个包含这个存在值的可选值,否则将返回nil:
|
|
39.我们还可以使用下标语法来通过给某个键的对应值赋值为nil来从字典里移除一个键值对:
|
|
40.此外,removeValueForKey(_:) 方法也可以用来在字典中移除键值对。这个方法在键值对存在的情况下会移除该键值对并且返回被移除的值或者在没有值的情况下返回nil:
|
|
41.我们可以使用 for-in 循环来遍历某个字典中的键值对。每一个字典中的数据项都以(key, value)元组形式返回,并且我们可以使用临时常量或者变量来分解这些元组:
|
|
42.通过访问 keys 或者 values 属性,我们也可以遍历字典的键或者值:
|
|
43.如果我们只是需要使用某个字典的键集合或者值集合来作为某个接受 Array 实例的 API 的参数,可以直接使用 keys 或者 values 属性构造一个新数组:
|
|
44.Swift 的字典类型是无序集合类型。为了以特定的顺序遍历字典的键或值,可以对字典的 keys 或 values 属性使用 sort() 方法。